Each Nadh That Enters the Electron Transport System
When you eat food your body goes through 3 phases for the food to become energy. Unlike in fermentation anaerobic respiration involves the formation of an electrochemical gradient by an electron transport system that results in the production of a number of ATP molecules.
All told the Krebs cycle forms per two molecules of pyruvic acid two ATP molecules ten NADH molecules and two FADH 2 molecules.
. This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy two pyruvate molecules two high energy electron-carrying molecules of NADH. FAD accepts two electrons becomes FADH2. Unlike in aerobic respiration the final electron recipient is a molecule other than oxygen.
Finally the high-energy electrons from NADH are passed along an electron-transport chain within the. Place the components of the electrontransport chain to outline the flow of electrons from NADH2 to O2. To the electron transport system.
NAD is a coenzyme of oxidation-reduction since it both accepts and gives up electrons. Now the molecule is ready to accept another acetyl-CoA molecule to begin another turn of the cycle. As we discuss shortly the acetyl group is oxidized to CO 2 in these reactions and large amounts of the electron carrier NADH are generated.
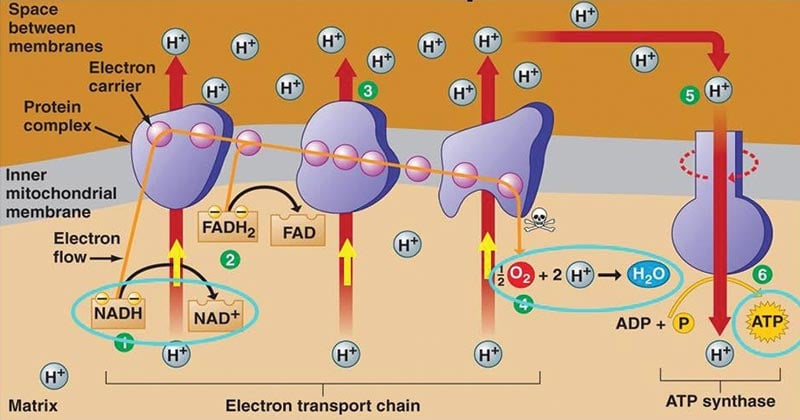
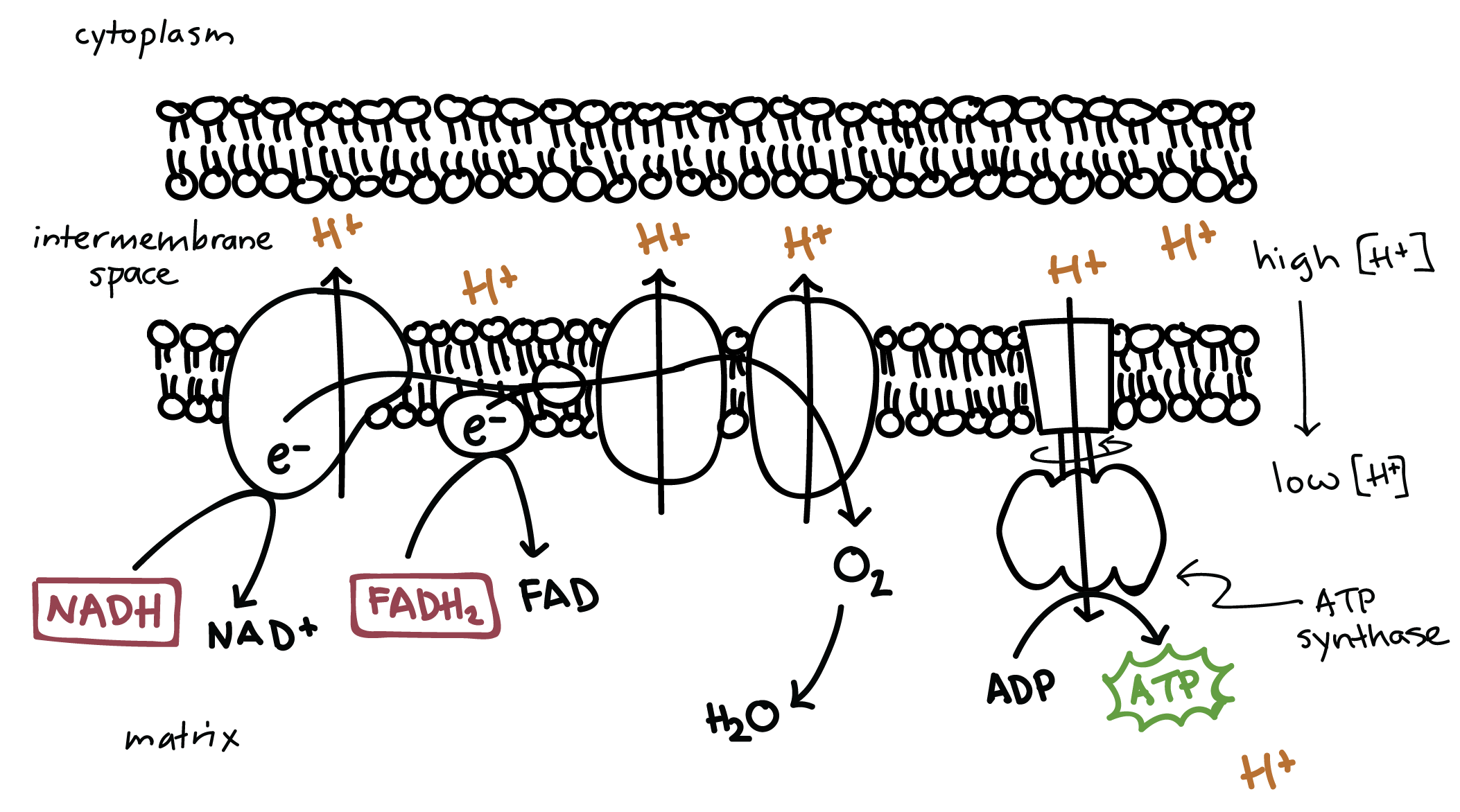
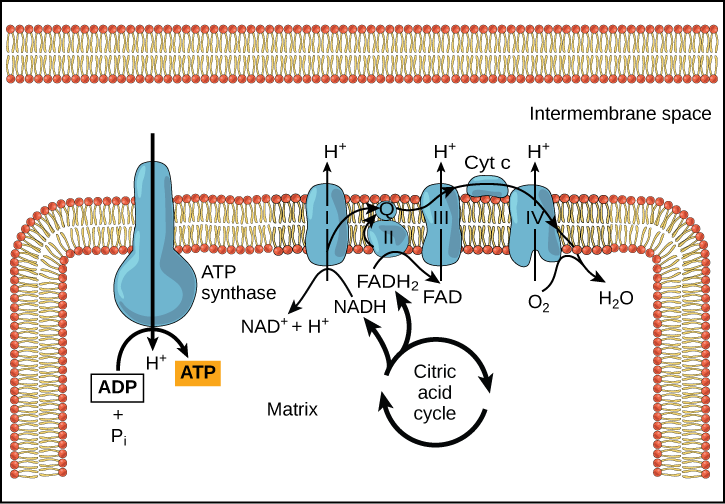
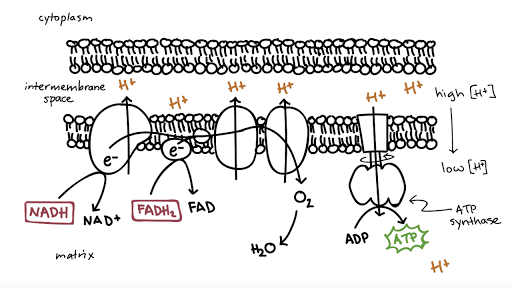
NADH and FADH2 then pass electrons through the electron transport chain in the mitochondria to generate more ATP molecules. Redox reductionoxidation ˈ r ɛ d ɒ k s RED-oks ˈ r iː d ɒ k s REE-doks is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of atoms are changed. The electrons are passed through a series of redox reactions with a small amount of free energy used at three points to transport hydrogen ions across a membrane.
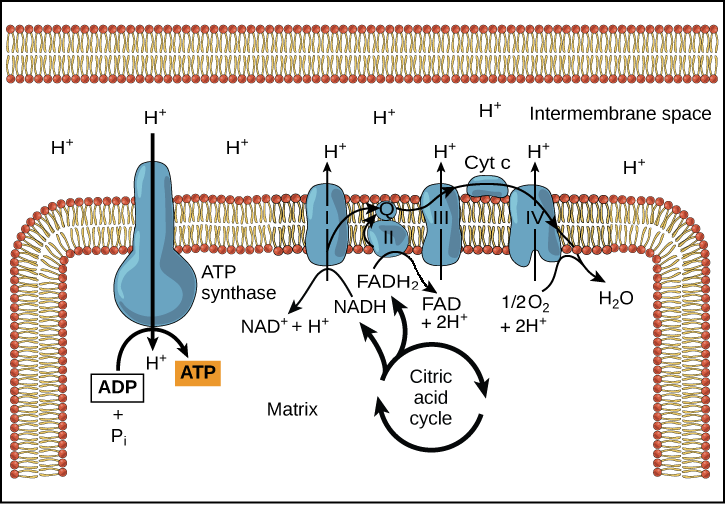
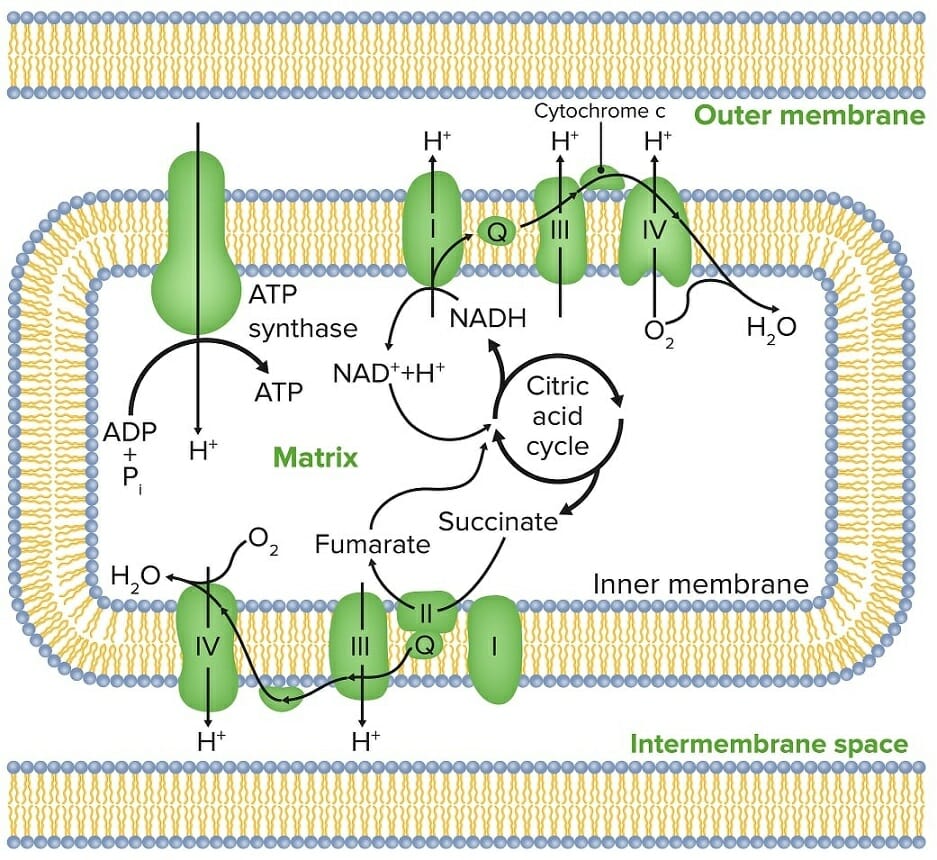
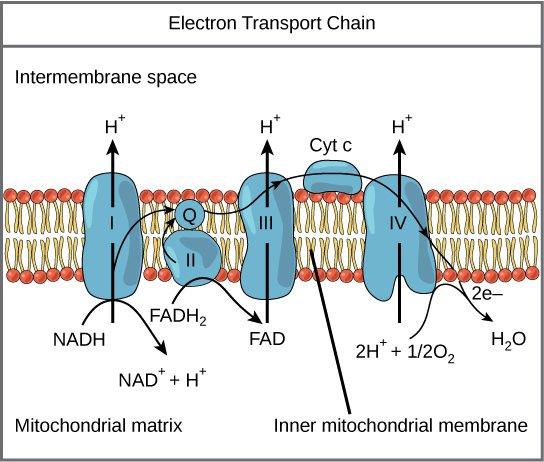
Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain During the first two phases NADH molecules will convert from NAD and in the third phase NADH molecules divide into NAD helping produce H and two electrons. Because this FADH 2 enters the electron transport chain at complex III it can fuel the extrusion of only six protons across the mitochondrial inner membrane. The electron transport chain is composed of four large multiprotein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and two small diffusible electron carriers shuttling electrons between them.
Cellular respiration has three steps each designed to generate NADH which carries electrons to the electron transport chain. The mitochondrial electron transport chain ETC consists of five protein complexes integrated into the inner mitochondrial membrane. FADH2 enters the chain a bit later during complex 2.
In glycolysis two NADH and two ATP are produced as are two pyruvate. The electron transport results in the formation of a proton gradient across the membrane which is utilised in the formation of ATP. The NADH and the FADH 2 will be used in the electron transport system.
The energy from the electron transport chain is. Thus using reducing equivalents shuttled this way the electron transport chain has an ATPNADH stoichiometry of only 15 ATP molecules per NADH molecule. After its transfer to the four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate the acetyl group enters a series of reactions called the citric acid cycle.
Match each name with the electrontransport chain complex or electron carrier. FAD coenzyme of oxidation-reduction can replace NAD. Many anaerobic organisms are obligate anaerobes.
Glycolysis which translates to splitting sugars is the process of releasing energy within sugars. Light energy causes the removal of an electron from a molecule of P680 that is part of Photosystem II. Here oxygen acts as the terminal electoral.
The TCA cycle in the mitochondrial matrix supplies NADH and FADH 2 to the ETC each of which donates a pair of electrons to the ETC via Complexes I and II respectively. Only a small amount of NAD is needed in cells. Learn the structure and balance of this chemical equation.
It comprises a series of enzyme complexes. During the Krebs cycle each pyruvate that is generated by glycolysis is converted into a two-carbon acetyl CoA molecule. The transfer of electrons from Complex I to.
Complex I is responsible for relieving NADH of its hydrogen and. The P680 requires an electron which is taken from a water molecule breaking the water into H ions and O-2 ions. Cellular respirationthe process of molecules being broken down into energy by cellscan be diagramed using chemical equations.
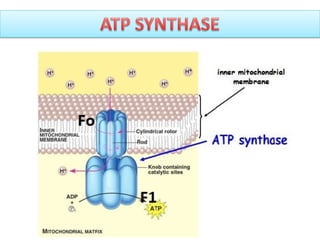
The H is used to create energy as ATP which then merges with the. Electron transport system and ATP synthase complex are present in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and plasma membrane of prokaryotes. The electron transport chain consists of four protein complexes simply named complex I complex II complex III and complex IV.
Each complex is designed to receive electrons from a coenzyme or one of the other complexes in the chain. Each NAD molecule is used over and over. When NADH moves through the transport chain about 10 H ions are pumped through the membrane so for each NADH 25 ATP can be made 10425.
In glycolysis a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain. The energy transfer is similar to the chemiosmotic electron transport occurring in the mitochondria.
The actions each complex takes can be seen in the image below. Redox reactions are characterized by the actual or formal transfer of electrons between chemical species most often with one species the reducing agent undergoing oxidation losing electrons while another species the. AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular.
Oxidative Phosphorylation And Electron Transport The Electron Transport Chain Sparknotes
Electron Transport Chain Etc Concise Medical Knowledge
How Are Protons Pumped Through The Oxidoreductase Complexes In The Electron Transport Chain Quora

Electron Transport Chain An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

6 26 Electron Transport Chain Nutrition Flexbook

Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy
How Many Atps Does An Electron Transport Chain Produce Quora
Electron Transport Chain Etc Components And Steps

The Mitochondrial Nadh Pool Is Involved In Hydrogen Sulfide Signaling And Stimulation Of Aerobic Glycolysis Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Lesson Explainer Oxidative Phosphorylation Nagwa

Citric Acid Cycle And Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology For Non Majors I
Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy
Electron Transport Chain Biology For Majors I

Electron Transport Chain Biology Quiz Quizizz
Reading Electron Transport Chain Biology I

6 26 Electron Transport Chain Nutrition Flexbook

Electron Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Dictionary
Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy
4 3 Citric Acid Cycle And Oxidative Phosphorylation Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Comments
Post a Comment